If you’ve ever wondered what is a CNC machine and why it has become a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, you’re not alone. CNC technology touches almost every industry, from automotive and aerospace to medical devices and consumer electronics. Whether you’re a manufacturing professional, an engineer, or simply curious about how everyday products are made, understanding what is a CNC machine can provide valuable insight into how precision components are created at scale.
In this article, we’ll break down what is a CNC machine, how it works, its different types, and why it has revolutionized the way products are designed and built.
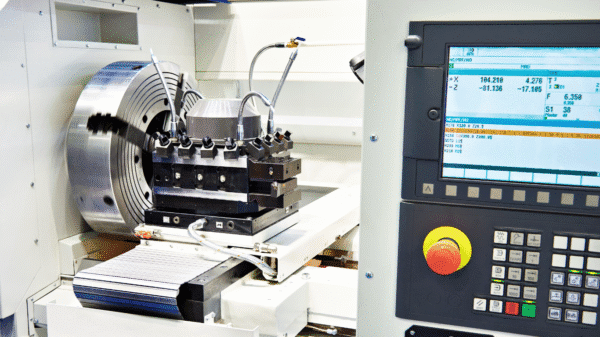
What is a CNC Machine?
At its core, a CNC machine, short for Computer Numerical Control machine, is a tool that uses computer programming to control machining operations. Instead of manual operation by a machinist, the machine follows digital instructions to cut, drill, mill, or shape materials with extreme precision.
When people ask what is a CNC machine, the simplest answer is this: it’s an automated manufacturing system that converts digital designs into physical parts with incredible accuracy. From custom metal components to complex 3D shapes, CNC machines are essential to producing consistent and high-quality products.
How Does a CNC Machine Work?
To fully understand what is a CNC machine, it helps to know how the process works:
-
Design Creation – The process starts with CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software, where an engineer creates a detailed model of the part.
-
Programming – The CAD file is converted into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) instructions, typically in G-code, which tells the CNC machine exactly how to move.
-
Machine Setup – The raw material (metal, plastic, wood, etc.) is secured in the machine, and the necessary tools are installed.
-
Execution – The CNC machine follows the programmed instructions, moving along multiple axes to cut, drill, or mill the part.
-
Quality Check – Once the part is completed, it’s inspected to ensure it meets the required tolerances and specifications.
When discussing what is a CNC machine, this workflow demonstrates why it’s such a vital technology—it removes human error, increases speed, and ensures repeatability across large production runs.
Types of CNC Machines
Answering what is a CNC machine also involves understanding the various types available. CNC machines come in different forms, each designed for specific tasks:
1. CNC Milling Machines
These machines use rotating cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece. They are ideal for producing complex shapes and precise components.
2. CNC Lathes
Lathes spin the workpiece while cutting tools shape it. They’re commonly used for symmetrical objects like shafts, bolts, and pulleys.
3. CNC Routers
Typically used for wood, plastic, and softer metals, CNC routers are excellent for large-scale cutting, engraving, and shaping.
4. CNC Plasma Cutters
These machines use a plasma torch to cut through conductive materials like steel or aluminum, perfect for heavy-duty fabrication.
5. CNC Laser Cutters
Laser cutters are extremely precise, using a focused laser beam to cut or engrave materials with intricate detail.
6. CNC EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
This method uses electrical sparks to erode material, often employed for hard metals and intricate molds.
Understanding these types helps clarify what is a CNC machine in different industries and applications.
Advantages of CNC Machines
Exploring what is a CNC machine isn’t complete without highlighting its benefits. CNC machines have transformed manufacturing for several reasons:
-
Precision and Accuracy – CNC machines achieve tolerances impossible for manual operations.
-
Efficiency – Automated processes reduce production time and labor costs.
-
Consistency – Each part produced is identical, ensuring high-quality results in mass production.
-
Complex Capabilities – CNC technology allows for intricate designs and 3D geometries.
-
Scalability – From prototypes to large production runs, CNC machines scale easily.
-
Reduced Waste – Accurate programming minimizes material waste, saving costs and resources.
These benefits explain why industries across the globe rely on CNC machines daily.
Applications of CNC Machines
To further answer what is a CNC machine, consider where they’re used:
-
Automotive – Engine components, transmission parts, and custom brackets.
-
Aerospace – High-precision parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
-
Medical – Surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment.
-
Electronics – Circuit boards, housings, and connectors.
-
Construction – Metal frameworks and architectural elements.
-
Consumer Products – Appliances, furniture, and sporting goods.
The versatility of CNC machines makes them indispensable across industries.
Why Understanding CNC Machines Matters
When asking what is a CNC machine, the real significance lies in its impact on modern life. Nearly every product you use daily—from your car to your smartphone—likely owes its existence to CNC technology. For businesses, embracing CNC machining means faster turnaround times, better product quality, and competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Choosing the Right CNC Partner
If your business needs CNC machining, partnering with an experienced manufacturer is essential. Companies like In-X Machine Inc. specialize in delivering high-precision CNC components tailored to your specifications. With expertise in various CNC technologies, they ensure every part meets strict quality standards and is delivered on time.
So, what is a CNC machine? It’s more than just a piece of equipment, it’s the backbone of modern manufacturing. CNC machines transform digital designs into tangible products with unmatched precision, efficiency, and reliability. Understanding this technology not only helps you appreciate the products around you but also empowers you to make informed decisions in manufacturing and engineering projects.
For high-quality CNC machining services that meet today’s demanding standards, In-X Machine Inc. is a trusted partner dedicated to precision, performance, and customer satisfaction.
 IN-X Machine, Inc.
IN-X Machine, Inc.